7 13 a the gage factor under tension is 3 5 at low strains and increases as the strain increases due to damage wang and chung 1997.
A strain gauge material should have low.
Its thickness should not exceed 10 micrometers.
The operation of the glue should isolate the wires from the material being tested.
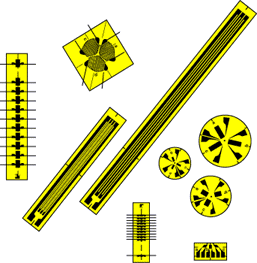
A strain gauge fig.
Simmons and arthur c.
A strain gauge material should have low a.
The glue used should be specially prepared for use in the strain gauge.
These metal foil strain gauge uses similar materials to wire strain gauges.
Polyimide is the prevalent backing material and is thus the default standard.
Bonded metal foil strain gauge.
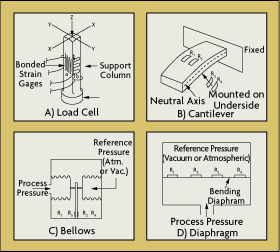
Strain gauge load cell.
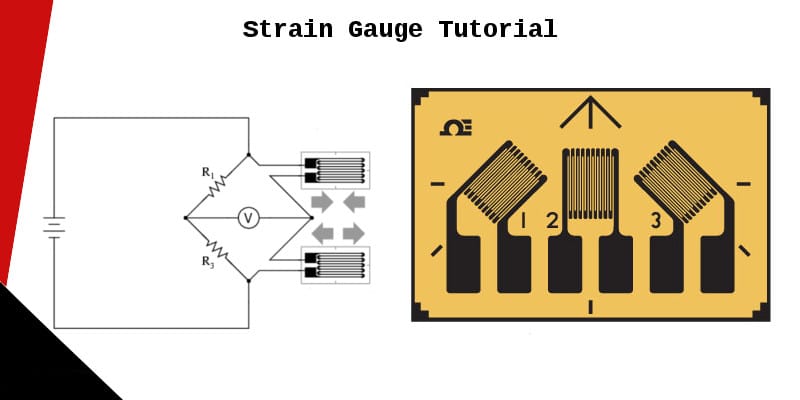
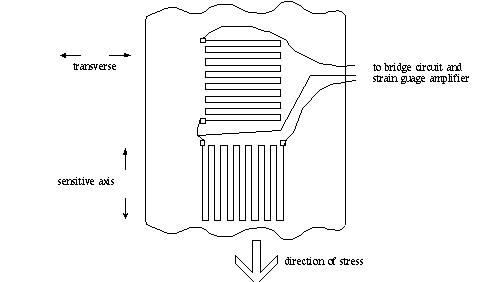
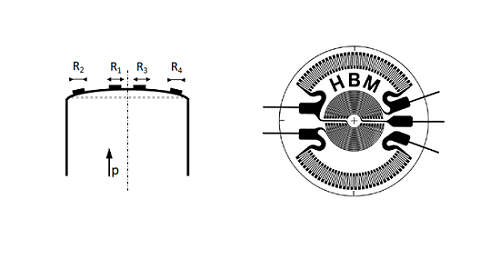
12 is a sensor which responds to the expansion or contraction of a material or the strain a strain gauge consists of a long thin piece of metal which folds back on itself or zig zags across the sensor.
This category is just an extension of previously defined bonded metal wire gauge.
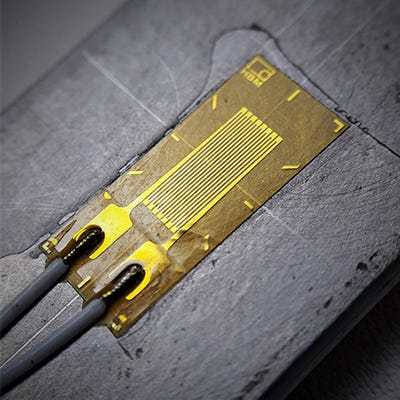
A strain gauge also spelled strain gage is a device used to measure strain on an object.
Ruge in 1938 the most common type of strain gauge consists of an insulating flexible backing which supports a metallic foil pattern.
Strain gauge load cells are the kind most often found in industrial settings.
The backing is usually made of a dielectric usually plastic which provides a good electrical insulation between the wires of the strain gage and the specimen.
The effectiveness of electrical resistance based strain sensing is inadequate due to the low value of the gage factor and the large effect of damage on the resistance even at high strains.
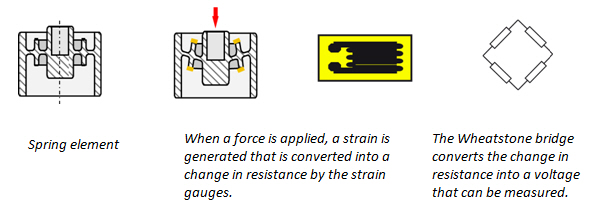
Structurally a load cell has a metal body to which strain gauges have been secured.
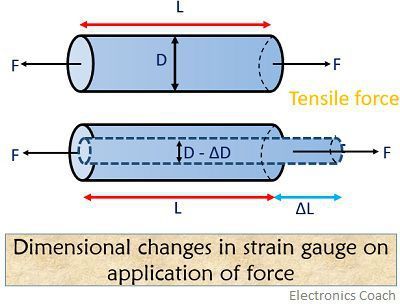
As the material expands or contracts the long thin piece of metal gets longer or shorter with the material changing the resistance of the metal.
It is ideal as it is highly accurate versatile and cost effective.
The strain gauge should be properly prepared by ideally gluing the strain gauge to the material being tested.
The linearity should be maintained within accuracy limits.
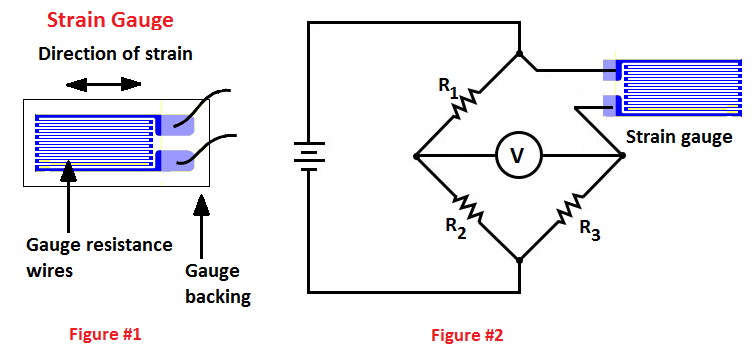
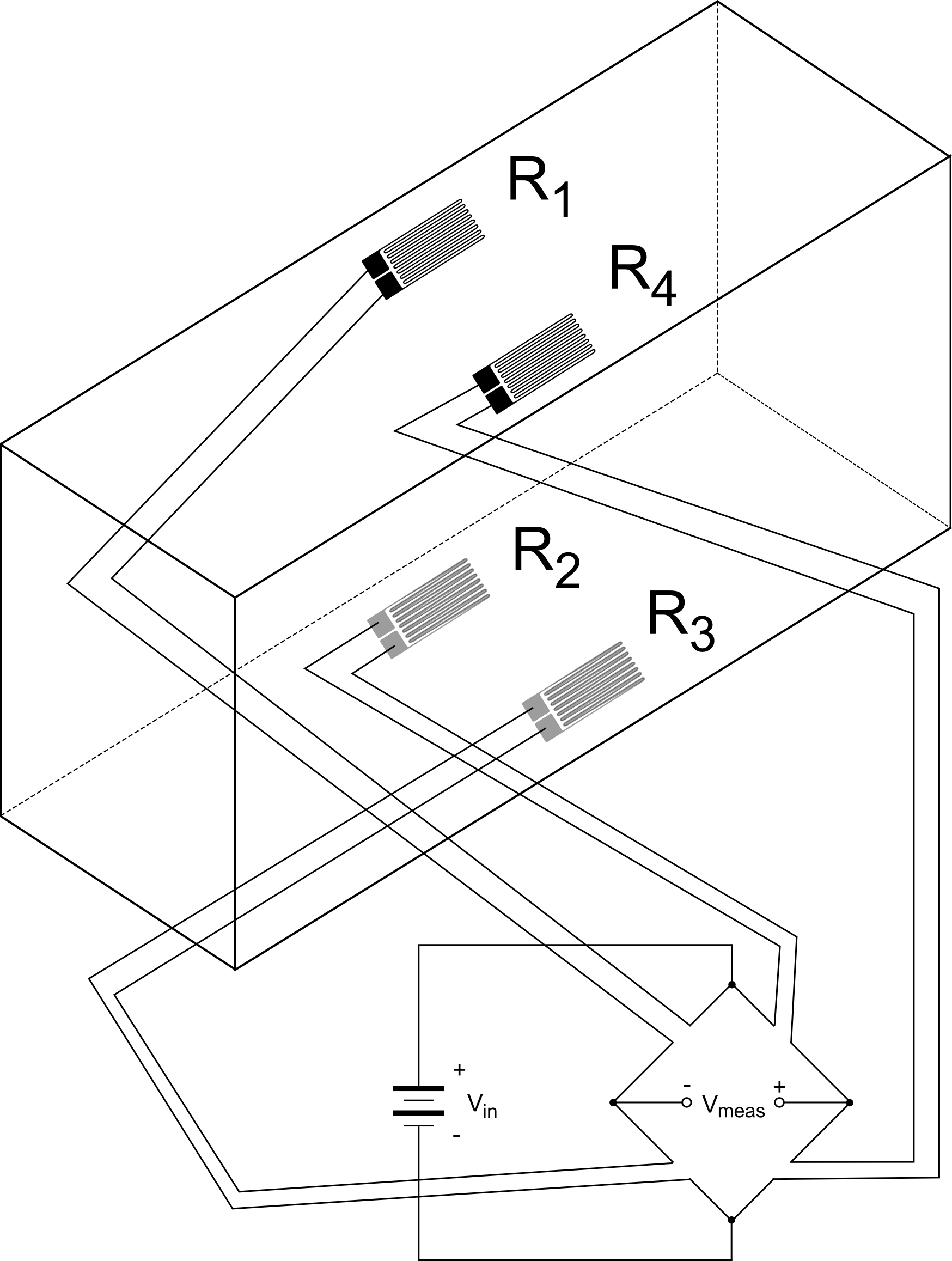
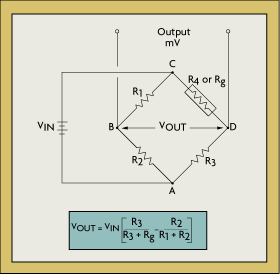
Measuring strain gauge circuits in order to measure strain with a bonded resistance strain gauge it must be connected to an electric circuit that is capable of measuring the minute changes in resistance corresponding to strain.
Strain gauges must have a good frequency response.
The gauge is attached to the object by a suitable adhesive such as cyanoacrylate.
Strain gauge transducers usually employ four strain gauge elements that are electrically connected to form a wheatstone bridge circuit.
Backing carrier materials are needed because strain gage wires are very fragile and difficult to handle.