Acid catalyzed hydration of phenyl acetylene a terminal alkyne involves a vinylic carbocation intermediate.
A secondary vinylic carbocation is.
Its empirical formula is c 2 h 3 more generally a vinylic cation is any disubstituted trivalent carbon where the carbon bearing the positive charge is part of a double bond and is sp hybridized in the chemical literature substituted vinylic cations are often referred to as vinyl cations and understood to.
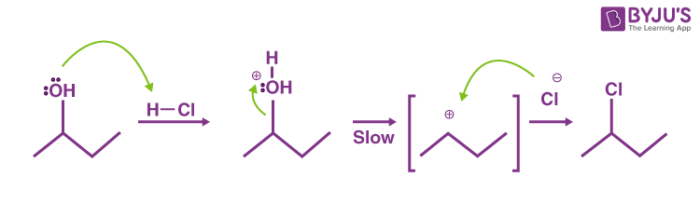
Secondary carbocations will require more energy than tertiary and primary carbocations will require the most energy.
The more substituted a carbocation is the more stable it is.
The carbocation bonded to three alkanes tertiary carbocation is the most stable and thus the correct answer.
The libretexts libraries are powered by mindtouch and are supported by the department of education open textbook pilot project the uc davis office of the provost the uc davis library the california state university affordable learning solutions program and merlot.
The allylic position is also like a vinylic position.
We also acknowledge previous national science foundation support under grant numbers 1246120 1525057 and 1413739.
The general formula for vinyl group is r ch ch 2 in which both carbon atoms are bonded with double bond and r is attached at vinylic position.
If in the more stable of the two resonance forms of an allylic carbocation the formal charge of 1 is on a secondary carbon the allylic carbocation is called a secondary 2 allylic carbocation.
If in both resonance forms the formal charge of 1 is on a secondary carbon it also is a secondary allylic carbocation.
This carbocation is also a benzylic carbocation.
The vinyl cation is a carbocation with the positive charge on an alkene carbon.